
Monkeypox Guidance Update
Posted June 21, 2022. Past health advisories and alerts are archived for historical purposes and are not maintained or updated.
The purpose of this advisory is to provide an update on the U.S. monkeypox outbreak and to provide clinical guidance to Spokane County healthcare providers. As this is a fairly long CDC Health Advisory, please, at a minimum, read the Recommendations for Clinicians section near the bottom of the document. We do encourage all providers who may see rash illness patients in their clinics to keep the entire document in a handy spot for reference. Please direct questions about testing any patients for monkeypox to SRHD at cdepi@srhd.org or call (509) 324-1442.
Summary
Since May 2022, monkeypox cases, which have historically been rare in the United States, have been identified in 18 states and territories among both persons returning from international travel and their close contacts domestically. Globally, more than 1,600 cases have been reported from more than 30 countries; the case count continues to rise daily. In the United States, evidence of person-to-person disease transmission in multiple states and reports of clinical cases with some uncharacteristic features have raised concern that some cases are not being recognized and tested.
This Health Alert Network (HAN) Health Update serves to alert clinicians to clinical presentations of monkeypox seen so far in the United States and to provide updated and expanded case definitions intended to encourage testing for monkeypox among persons presenting for care with relevant history, signs, and symptoms. In addition, this Health Update provides an update to a HAN Health Advisory that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued May 20, 2022 titled Monkeypox Virus Infection in the United States and Other Non-endemic Countries—2022. In people with epidemiologic risk factors, rashes initially considered characteristic of more common infections (e.g., varicella zoster, herpes, syphilis) should be carefully evaluated for concurrent characteristic monkeypox rash (see images and links to below) and considered for testing.
Background
The current identification of West African monkeypox cases in many countries that do not have endemic disease and involving patients with no direct travel history to an area with endemic monkeypox, suggests person-to-person community spread. The first case of monkeypox in the United States was diagnosed in a traveler who returned to Massachusetts from Canada on May 17, 2022. Since then, 65 cases have been identified in 18 states and territories and more than 1,600 have been identified in 35 countries and territories that do not have endemic disease. The case fatality rate of monkeypox associated with the West African clade of monkeypox virus is 1%, and possibly is higher in immunocompromised individuals; no deaths have been reported globally from the current outbreak. Any person, irrespective of gender identity or sexual orientation, can acquire and spread monkeypox. In this outbreak, however, many of the reported cases in the United States are among gay, bisexual, or other men who have sex with men (MSM). Close contact, sustained skin-to-skin contact including sexual contact, with a person with monkeypox or contact with contaminated fomites (e.g., shared linens) are the most significant risk factors associated with human-to-human transmission of Monkeypox virus.
Updated Case Definitions
- On June 1, 2022, CDC updated and expanded its monkeypox case definitions to ensure that anyone who is suspected of having monkeypox can be tested and appropriate steps to protect contacts can be taken.
- Revised categories of suspected, probable, and confirmed cases of monkeypox standardize case reporting through the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS). In addition, the “suspected” case definition encourages broader suspicion for monkeypox.
| Clinical and laboratory classification | Criteria |
| Suspected | New characteristic rash* OR |
| Meets one of the epidemiologic criteria and has high clinical suspicion† for monkeypox | |
| Probable | No suspicion of other recent Orthopoxvirus exposure (e.g., Vaccinia virus in ACAM2000 vaccination) AND demonstration of the presence of |
| |
| Confirmed | Demonstration of the presence of Monkeypox virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction testing or Next-Generation sequencing of a clinical specimen OR |
| Isolation of Monkeypox virus in culture from a clinical specimen | |
| Epidemiologic classification | |
| Within 21 days of illness onset: | Reports having contact with a person or persons with a similar appearing rash or with a person who has received a diagnosis of confirmed or probable monkeypox OR |
| Had close or intimate in-person contact with persons in a social network experiencing monkeypox infections. This includes MSM who meet partners through an online website, digital application (“app”), or social event (e.g., a bar or party) OR | |
| Traveled, within 21 days of illness onset outside the United States to a country with confirmed cases of monkeypox or where Monkeypox virus is endemic OR | |
| Had contact with a dead or live wild animal or exotic pet that is an African endemic species, or used a product derived from such animals (e.g., game meat, creams, lotions, powders, etc.) | |
| Exclusions | |
| A case might be excluded as a suspected, probable or confirmed case if: | An alternative diagnosis* can fully explain the illness OR |
| A person with symptoms consistent with monkeypox does not develop a rash within 5 days of illness onset OR | |
| A case where high-quality specimens do not demonstrate the presence of Orthopoxvirus or monkeypox virus or antibodies to Orthopoxvirus | |
| *The characteristic rash associated with monkeypox lesions involves the following: deep-seated and well-circumscribed lesions, often with central umbilication; and lesion progression through specific sequential stages: macules, papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs. The rash can sometimes be confused with other diseases that are more commonly encountered in clinical practice (e.g., syphilis, herpes, and varicella zoster). Historically, sporadic accounts of patients co-infected with monkeypox virus and other infectious agents (e.g., varicella zoster, syphilis) have been reported; so patients with a characteristic rash should be considered for monkeypox virus testing, even if tests for other infectious agents are positive. † Clinical suspicion may exist if lesions consistent with those from more common infections (e.g., syphilis, herpes, and varicella zoster) co-exist with lesions that may be characteristic of monkeypox. | |
Clinical presentations of confirmed cases to date
Descriptions of classic monkeypox disease describe a prodrome including fever, lymphadenopathy, headache, and muscle aches followed by development of a characteristic rash culminating in firm, deep-seated, well-circumscribed and sometimes umbilicated lesions. The rash usually starts on the face or in the oral cavity and progresses through several synchronized stages on each affected area and concentrates on the face and extremities, including lesions on the palms and soles.
Thus far in the U.S. outbreak, all patients diagnosed with monkeypox in the United States have experienced a rash or enanthem. Although the characteristic firm, deep-seated, well-circumscribed and sometimes umbilicated rash has been observed, the rash has often begun in mucosal areas (e.g., genital, perianal, oral mucosa) and in some patients, the lesions have been scattered or localized to a specific body site rather than diffuse and have not involved the face or extremities. In some instances, patients have presented with symptoms such as anorectal pain, tenesmus, and rectal bleeding which upon physical examination, have been found to be associated with visible perianal vesicular, pustular, or ulcerative skin lesions and proctitis. The lesions have sometimes been in different stages of progression on a specific anatomic site (e.g., vesicles and pustules existing side-by-side), In addition, prodromal symptoms including fever, malaise, headache, and lymphadenopathy have not always occurred before the rash if they have occurred at all.
The clinical presentation of monkeypox may be similar to some STIs, such as syphilis, herpes, lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), or other etiologies of proctitis. Clinicians should perform a thorough skin and mucosal (e.g., anal, vaginal, oral) examination for the characteristic vesiculo-pustular rash of monkeypox; this allows for detection of lesions the patient may not have been previously aware of. The search for lesions consistent with monkeypox should be performed even if lesions consistent with those from more common infections (e.g., varicella zoster, syphilis, herpes) are observed; this is particularly important when evaluating patients who have epidemiologic risk factors for monkeypox. Specimens should be obtained from lesions (including those inside the mouth, anus, or vagina) and tested for monkeypox.
Any patient who meets the suspected case definition should be counseled to implement appropriate transmission precautions. Probable and confirmed case-patients should remain in isolation for the duration of their infectious period (i.e., until all lesions have resolved, the scabs have fallen off, and a fresh layer of intact skin has formed). Patients who do not require hospitalization but remain potentially infectious to others should isolate at home. This includes abstaining from contact with other persons and pets, and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (e.g., clothing to cover lesions, face mask) to prevent further spread.
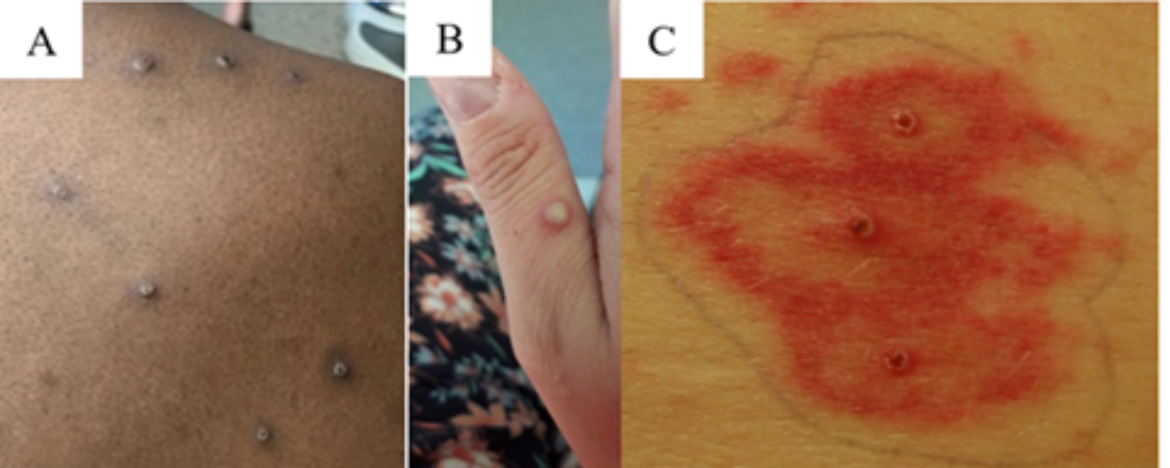
Generalized monkeypox lesions are characteristically deep-seated, well-circumscribed, and often develop umbilication (A, B, C), Image A demonstrates both papulovesicular and pustular lesions in the same region of the body. Credits: Images A and B from NHS England High Consequence Infectious Diseases Network; image C from Reed KD, Melski JW, Graham MB et al. The detection of monkeypox in humans in the Western Hemisphere. Page 346. Copyright © 2004. Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission. Please see lesion examples from Nigeria and Italy.
Recommendations for Clinicians
- Patients with rashes initially considered characteristic of more common infections (e.g., varicella zoster or sexually transmitted infections) should be carefully evaluated for a characteristic monkeypox rash (see images and links), and submission of specimens of lesions should be considered, especially if the person has epidemiologic risk factors for monkeypox infection.
- Evaluate any individual presenting with perianal or genital ulcers, diffuse rash, or proctitis syndrome for STIs per the 2021 CDC STI Treatment Guidelines. Testing for STIs should be performed. The diagnosis of an STI does not exclude monkeypox as a concurrent infection may be present. The clinical presentation of monkeypox may be similar to some STIs, such as syphilis, herpes, lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), or other etiologies of proctitis.
- Clinicians should perform a thorough skin and mucosal (e.g., anal, vaginal, oral) examination for the characteristic vesiculo-pustular rash of monkeypox; this allows for detection of lesions the patient may not have been previously aware of.
- If a patient does not respond to STI treatment as expected, the patient should return for follow-up evaluation and monkeypox testing should be considered.
- Please refer to the most recent CDC guidance for specimen collection to ensure proper collection of specimens.
- In addition to dry swabs, CDC can now accept lesion swabs in viral transport media and lesion crusts (currently these two specimens must be received by CDC within 7 days of collection).
- Clinicians should use appropriate infection prevention measures when collecting specimens for monkeypox evaluation. Information on infection prevention and control in healthcare settings is provided on the CDC website.
- Advise patients with prodromal symptoms (e.g., fever, malaise, headache) and one or more epidemiologic risk factors for monkeypox to self-quarantine. If a rash does not appear within 5 days, the illness is unlikely to be monkeypox and alternative etiologies should be sought.
- Clinicians should consult their local health department 509-324-1442 or CDEpi@srhd.org if they suspect monkeypox.
- All laboratory specimens should be sent through the state and territorial public health department, unless authorized to send them directly to CDC.
For More Information
- Case Definitions for Use in the 2022 Monkeypox Response
- Information for Healthcare Professionals
- Clinical Recognition of Monkeypox
- Monitoring Persons Who Have Been Exposed
- Monkeypox Outbreak — Nine States, May 2022
- U.S. Monkeypox 2022: Situation Summary
- Monkeypox facts for people who are sexually active
