
Vaccination to Prevent COVID-19 Outbreaks with Current and Emergent Variants
Posted July 29, 2021. Past health advisories and alerts are archived for historical purposes and are not maintained or updated.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is notifying public health practitioners and clinicians about the urgent need to increase COVID-19 vaccination coverage across the United States to prevent surges in new infections that could increase COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality, overwhelm healthcare capacity, and widen existing COVID-19-related health disparities. Increasing vaccination coverage is especially urgent in areas where current coverage is low. Unvaccinated persons account for the majority of new COVID-19 infections, hospitalizations, and deaths. Currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, especially the highly infectious Delta variant (B.1.617.2), are accelerating spread of infection. Unvaccinated and partially vaccinated people need to practice all recommended prevention measures until fully vaccinated. In areas with substantial and high transmission, CDC recommends that fully vaccinated individuals wear a mask in public indoor settings to help prevent the spread of Delta and protect others.
Background
COVID-19 case rates are rising again after a period of decline: COVID-19 cases have increased over 300% nationally from June 19 to July 23, 2021, along with parallel increases in hospitalizations and deaths driven by the highly transmissible B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant. While significant progress has been made to make COVID-19 vaccine widely available, disparities in vaccination coverage persist across population groups and geographic areas. As of July 23, 2021, 1,856 (63.0%) of the 2,945 counties with available vaccination data have particularly low vaccination coverage, defined here as <40% of the population being fully vaccinated. As of July 23, 2021, 36% of the counties with vaccine coverage <40%, have COVID-19 incidence rates in the high burden level (≥100 cases/100,000 over the last seven days)
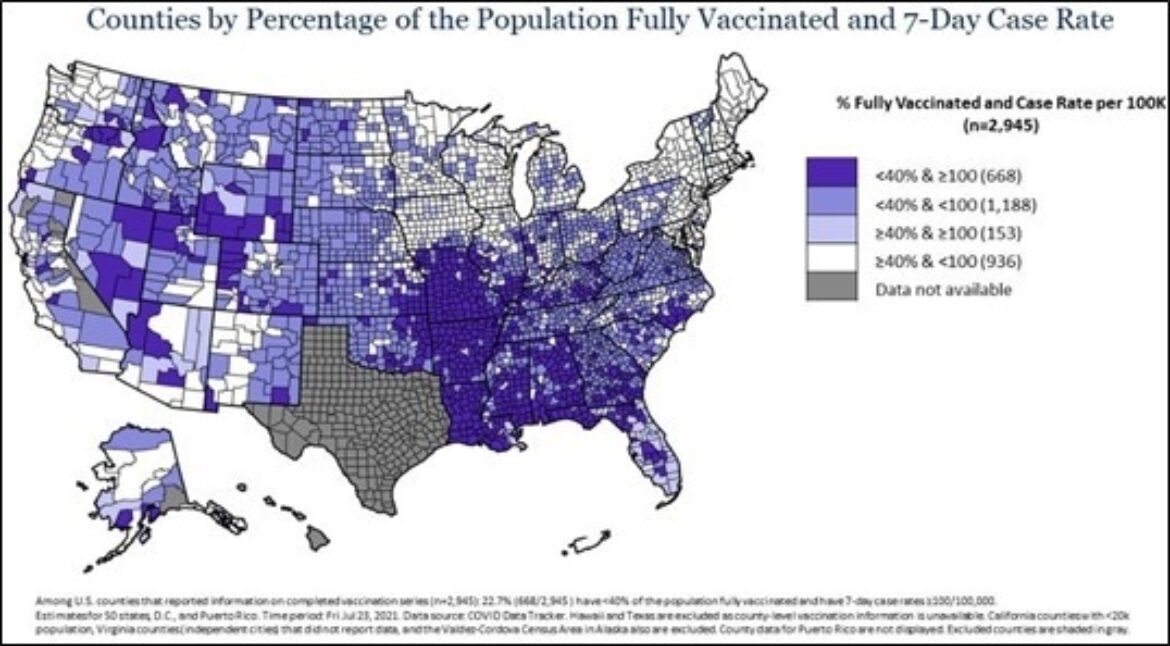
Overall, the majority (81.4%) of counties with high COVID-19 incidence rates are found in communities with low vaccination coverage. As COVID-19 case counts continue to rise nationally, areas with lower vaccination coverage are at especially high risk for a surge in cases. (see map and further data at COVID Tracker).
Most cases of COVID-19 and hospitalizations are in unvaccinated individuals:
The majority of COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations are occurring among individuals who are not fully vaccinated. From January through May 2021, of the more than 32,000 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19-associated hospitalizations in adults ≥18 years of age for whom vaccination status is known, <3% of hospitalizations occurred in fully vaccinated persons.
The COVID-19 Delta variant is widely prevalent and more infectious than prior strains: The COVID- 19 Delta variant currently accounts for more than 80% of all COVID-19 cases in the United States. This variant is significantly more infectious than prior SARS-CoV-2 variants and has led to a rapid rise in COVID-19 cases in other countries, including the United Kingdom and Israel. Emerging evidence suggests that fully vaccinated people who do become infected with the Delta variant are at risk for transmitting it to others.
COVID-19 vaccination is our most effective strategy to prevent infection and severe disease:
Immunologic data support the role of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-authorized COVID-19 vaccines in offering protection against the known currently circulating variants. By limiting viral spread, vaccination also minimizes opportunities for the introduction of more infectious variants through random mutation.
Mutations could produce future variants that are more virulent and capable of evading diagnostic and therapeutic tools or overcoming vaccine-induced immunity.
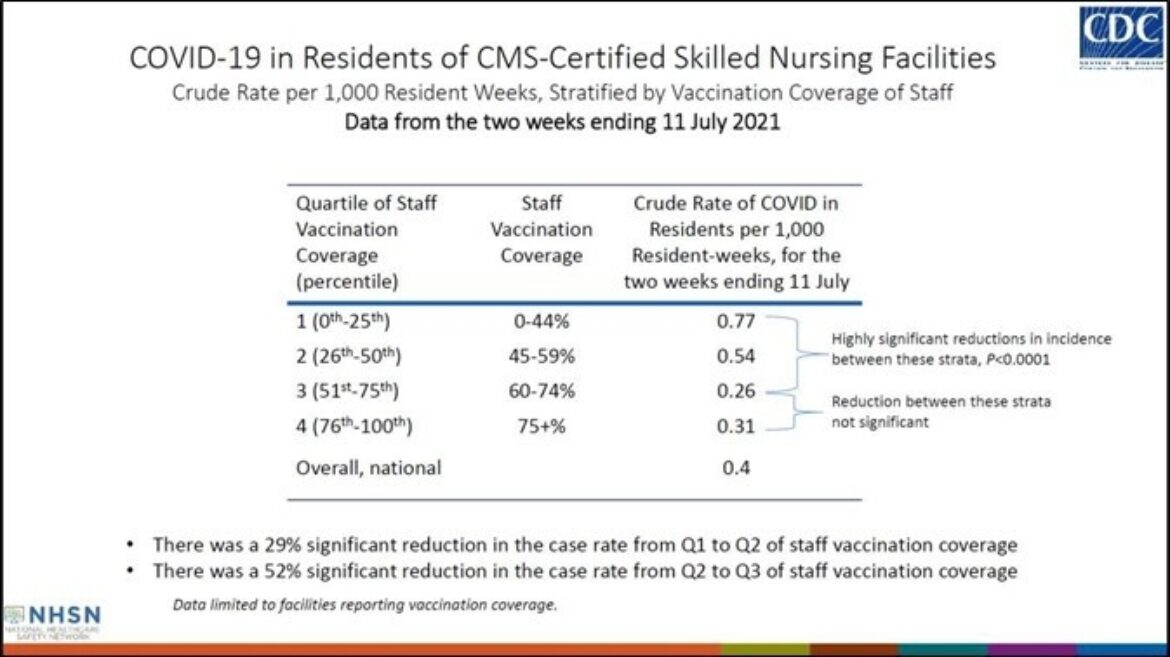
COVID-19 vaccination coverage at skilled nursing facilities (SNF) helps prevent infection: Nursing home residents have been severely impacted by COVID-19 and are disproportionately represented in overall burden of COVID-19-related morbidity and mortality in the United States. While there has been significant progress in vaccinating SNF residents, vaccination coverage of staff at many facilities remains low. Preliminary data from CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) indicate residents of SNFs in which vaccination coverage of staff is 75% or lower experience higher crude rates of preventable COVID infection.
Recommendations for Clinicians
- If you are a clinical provider and are not fully vaccinated, get vaccinated as soon as possible to protect yourself, your family, and your patients.
- Increase patient outreach efforts to encourage, recommend, and offer COVID-19 vaccination.
- Remind patients that vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 12 years of age and older, even for those with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. Follow trusted sources carefully for any new recommendations and changes in vaccine guidance.
- People who are immunocompromised should be counseled about the potential for reduced immune responses to COVID- 19 vaccines and to follow current prevention measures to protect themselves against COVID-19 until advised otherwise by their healthcare provider.
- Support efforts to ensure people receiving a first dose of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (i.e., Pfizer- BioNTech or Moderna) return for their second dose to complete the series.
- Communicate with unvaccinated staff, patients, and other individuals to increase confidence in vaccination. CDC has many resources for providers to help increase vaccine confidence.
- Recommend that fully vaccinated patients who are immunocompromised continue to practice all recommended prevention measures for unvaccinated persons.
Recommendations for Healthcare Facilities and Systems, Nursing Homes, and Businesses
- Recommend and offer COVID-19 vaccine to your staff and employees and establish policies to encourage uptake such as time off to receive the vaccine.
- Consider offering COVID-19 vaccine at your workplace (Workplace COVID-19 Vaccine Toolkit).
- Evaluate whether your facility can implement vaccine requirements or vaccine incentives.
For More Information
- CDC Weekly Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) Guidance for Implementing COVID-19 Prevention Strategies in the Context of Varying Community Transmission Levels and Vaccination Coverage
- Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People
- COVID Data Tracker
